Intro to Networking - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Overview
This is an introductory article on the workings of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
NOTES:
Find a complete introductory guide on Routing and Switching in our Ubiquiti Broadband Routing & Switching Specialist (UBRSS) guide, downloadable in our Training section.
DHCP Introduction
DHCP is used to dynamically assign IP address and other parameters (DHCP options) to devices on the network. The protocol uses both UDP port 67 (server) and UDP port 68 (client) and several different message types:
DiscoverDHCP clients send DHCP Discover messages to find a DHCP server (broadcast).OfferThe DHCP server responds to the Discover message with a DHCP Offer (unicast).RequestThe client replies to the server with a Request message and requests previously the offered address (broadcast).AckThe server accepts the Request from the client and responds with a DHCP Ack (acknowledgment) message.
In addition to the offered IP address, the server can also provide the following DHCP options to the client:
Subnet MaskThe subnet mask used by the network (for example 255.255.255.0).Router AddressThe address of the default gateway.DNS Server(s)The DNS servers that the clients should use to resolve names.Lease TimeThe time that the address is valid (for example 1 day).Custom OptionsOther options provided by the server, such as a TFTP server or the location of the UniFi Network application.
The diagram below shows an example of the DHCP message exchange process between the client and the server:
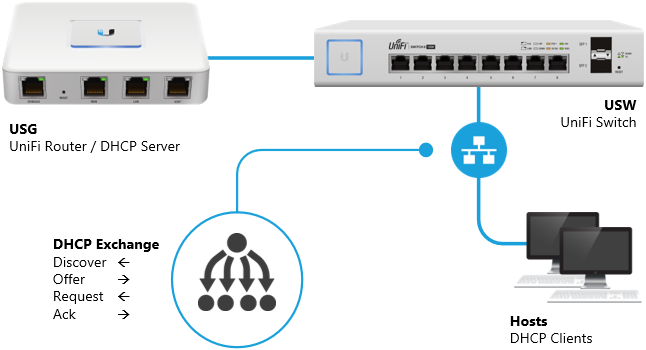
Example setup where the DHCP server is running on the UniFi Security Gateway (USG). The clients will send a DHCP Discover broadcast message, to which the server responds with a unicast DCHP Offer message.